Data Silos and Fabric Solution
In a world where data is considered the new oil, managing it effectively becomes a strategic imperative for any company wishing to remain competitive. However, many organisations still face the challenge of data silos - a persistent problem that can inhibit the ability to extract real value from the data collected. This article explores the concept of data silos, their implications and how Fabric can offer an effective solution to this problem.
What are Data Silos?
Data silos occur when data sets are stored in isolation and managed by different departments within an organisation, without an effective sharing or integration strategy. This fragmentation not only makes it difficult to access information, it also reduces operational efficiency, makes it difficult to analyse data and can lead to decisions being made based on incomplete or outdated information.

Implications of Data Silos
Data silos create a number of complications that can adversely affect an organisation's operations, strategy and efficiency. Let's explore the implications of data silos in more depth with practical examples that illustrate the problems faced by companies, they are vast and varied, including:
- Operational Inefficiencies: When data is not shared between departments, each team can end up replicating efforts to collect and analyse the same information.
- Difficulties in Decision-Making: The lack of a holistic vision can lead to decisions that don't consider all the relevant variables, potentially jeopardising the company's performance.
- Compliance problems: With data regulations becoming increasingly strict, data silos can complicate compliance with regulations, exposing the company to legal and financial risks.
Examples of the Implications of Data Silos
- Operational Inefficiencies
Example: In a large corporation, the marketing department may keep customer data in one system, while customer service uses another system without access to marketing information. This lack of integration can result in marketing campaigns that don't take into account recent customer interactions with support, resulting in repetitive or irrelevant communications that frustrate customers and waste resources.
- Decision-making difficulties
Example: A manufacturing company may have production data stored separately from sales and supply data. When demand for a product increases, the lack of an integrated view can delay the production response due to not immediately detecting the increase in demand. This can lead to lost revenue due to the inability to meet market demand in a timely manner.
- Compliance issues
Example: In the financial sector, regulations require companies to keep a detailed history of all transactions and communications with clients. If this information is scattered across several incompatible systems, it can be extremely difficult to respond to regulatory requests quickly and completely, which can result in significant penalties.
- High Maintenance and Integration Costs
Example: A company that uses different systems for each of its departments can face high costs when trying to integrate these platforms. Developing customised interfaces to allow the systems to communicate can be expensive and often results in interim solutions that are not sustainable in the long term.
- Barriers to Innovation
Example: A technology company may have several teams working on similar solutions with no knowledge of each other due to the separation of data and communications. This not only duplicates effort and wastes resources, but also prevents the company from innovating effectively by not taking advantage of synergies between departments.
- Data Quality and Consistency Compromised
Example: In the healthcare sector, clinical information may be stored separately from patients' administrative information. If this data is not consistently synchronised, treatments may be administered based on outdated information, which increases the risk of medical errors.
The Importance and Advantages of Data Governance
Data governance is a set of processes, policies, standards and metrics that guarantee the effective and efficient management of an organisation's data. In a scenario where data is a crucial strategic asset, data governance takes on vital importance to ensure that data is used appropriately, securely and efficiently, helping to avoid problems such as data silos. Below, we detail the importance and main advantages of implementing solid data governance.
- Compliance and Regulation: In many industries, especially in the financial, health and utilities sectors, compliance with legal and regulatory standards is essential. Data governance ensures that data is managed in accordance with applicable laws and regulations, helping to avoid legal sanctions and fines.
- Data quality: Incorrect or outdated data can lead to ill-informed and potentially disastrous business decisions. Data governance focuses on the accuracy, consistency and integrity of data throughout the organisation.
- Data Security: Protecting data from unauthorised access and leakage is a priority in any business environment. Data governance establishes security policies that help protect sensitive and confidential data.
- Facilitating Data Management: Data governance provides a framework that helps manage data access, storage, archiving and deletion, ensuring that data resources are optimised and costs are controlled.
Advantages of Data Governance
- Elimination of Data Silos: Data governance promotes the integration of data throughout the organisation, reducing the fragmentation of data into silos that can isolate critical information and hinder data analysis. This is achieved by defining policies that regulate data storage and facilitate sharing and accessibility.
- Improved Decision-Making: With high-quality, easily accessible data, decision-makers can trust that they are using accurate, up-to-date information, leading to more informed and effective decisions.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: By reducing duplication and improving data quality, data governance allows operations to become more efficient. Automated processes and fewer data errors mean that less time and resources are wasted.
- Improved Transparency: Data governance increases transparency in the use and management of data, which is crucial for both internal trust and the company's external reputation.
- Fostering Innovation: With well-managed and easily accessible data, organisations can more easily explore new opportunities, carry out advanced analyses and develop new products or services.
Possible solutions
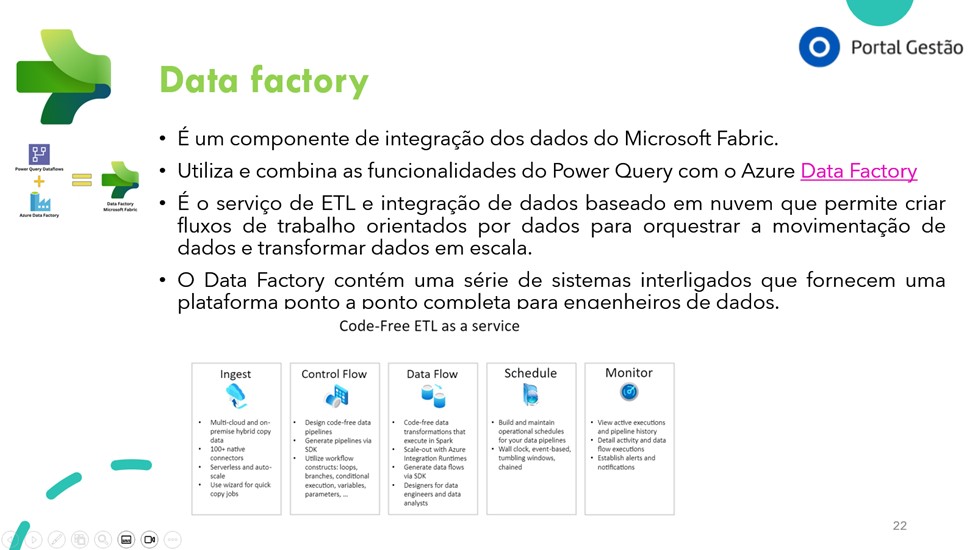
Microsoft Fabric is a complete, cloud-based SaaS solution for data and analyses.
It is built on top of an open lake (OneLake) and unites various Microsoft tools to simplify all data and analysis workflows, from integration and data engineering to data science.
Microsoft launched Fabric at the latest Microsoft Build on 23 May 2023.
What is Microsoft Fabric?
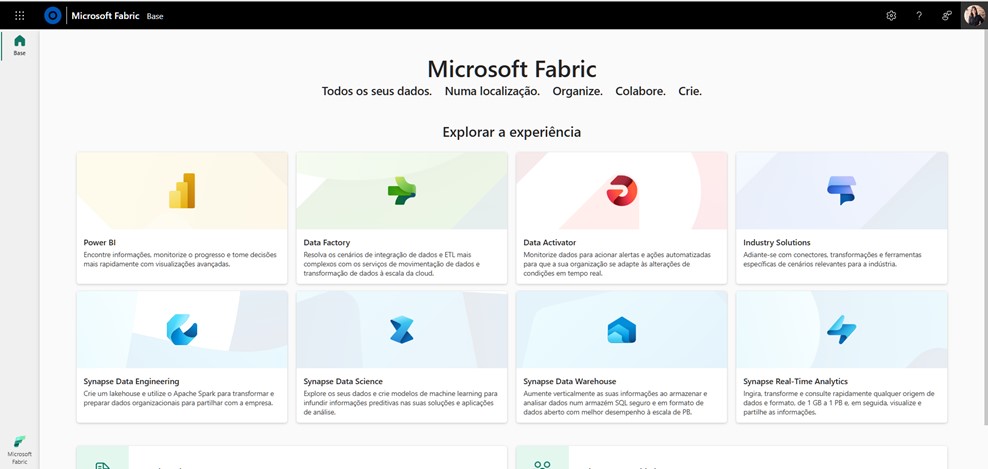
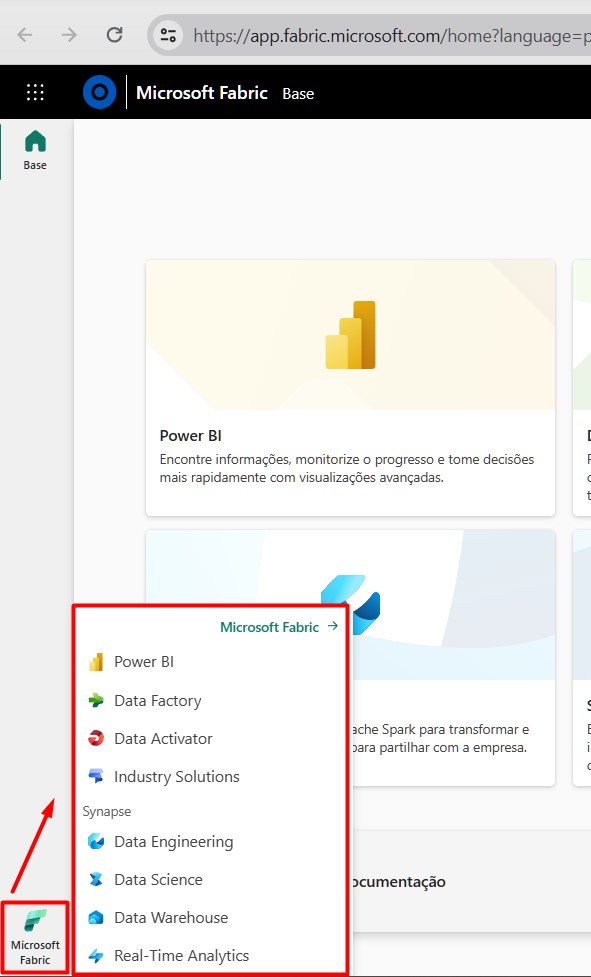
Microsoft Fabric is a cloud-based SaaS offering that brings together various data and analysis tools that organisations need. These include
- Data Factory,
- Synapse Data Warehouse,
- Synapse Data Engineering,
- Synapse Data Science,
- Synapse Real-Time Analytics,
- Power BI and
- Data Activator
- Industry Solutions
Fabric is built on an open, lake-centred design with a central multi-cloud repository called OneLake.
Microsoft Fabric supports open data formats across all its workloads and tiers, caters for technical and corporate data professionals and has customers such as T-Mobile, Ferguson and Aon.
Microsoft Fabric brings together the best parts of data mesh, data fabric and data hub to provide a one-stop shop for data integration, data engineering, real-time analysis, data science and business intelligence without compromising the privacy and security of your data.

In your Power BI Service, look in the start menu for the Fabric symbol:
Advantages of Fabric
- With Microsoft Fabric, you don't have to spend all your time combining various services from different suppliers.
- It removes data silos and the need to access multiple systems, improving collaboration between data professionals.
- Fabric offers persona-optimised experiences and tools in an integrated user interface.
- In addition to a simple, shared user experience, Fabric is a unified software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering, with all your data stored in a single open format in OneLake.
- Fabric offers scalability, economy, accessibility from anywhere with an Internet connection and continuous updates and maintenance provided by Microsoft.



Conclusion
Implementing robust data governance is fundamental for any organisation wishing to maximise the value of its data. As well as preventing data silos from forming, good data governance ensures that information is a powerful and secure asset that supports efficient business operations and continuous innovation. Therefore, data governance is not only an operational and regulatory necessity, but also a strategic lever that can distinguish a company in today's competitive market.
And Fabric's resources are attractive for centralising information and data professionals. It is a comprehensive ecosystem that is concerned with the unification and governance of data in order to distribute it in a secure and performant way to professionals.
In our Power BI Level 1 Plus training we covered a little about Fabric, especially Data Factory, which allows us to carry out the data pipeline process and create Data Flows.
You might ask: "What's the difference between Data Pipeline and Dataflow? Are they both doing the same thing? Should I use one over the other?" Here I'm answering that question.
Dataflows and Data Pipelines are not substitutes for each other, but complement each other.
Dataflows are for data transformation. They use Power Query transformations to get the data from the source and bring it in the required shape and format to the destination.
Data pipelines are for controlling the flow of execution. They use control flow activities, such as loops, conditions, etc., to place data transformations in the larger context of an ETL job. They are complements to data flows.